News
News
Sysmex Wins Awards in 2010 Kinki Local Commendation for Invention
Sysmex Corporation (HQ: Kobe, Japan; President: Hisashi Ietsugu) received several awards at the 2010 Kinki Local Commendation for Invention, sponsored by the Japan Institute of Invention and Innovation. The company received the Commissioner of the Japan Patent Office Invention Incentive Award for one invention, and Invention and Innovation Encouragement Awards for three other inventions. Local commendations for invention, which are awarded to engineers and researchers who create superior technologies and designs, have a history spanning 89 years. This marks the 12th consecutive year in which Sysmex has received local commendations for its inventions.
(1) Commissioner of the Japan Patent Office Invention Incentive Award
White blood cell classification and counting method and reagent kit (Patent number: 4248017)
This invention relates to the reagent kit and the method used by the reagent kit for classification and counting of white blood cells employed in the XE, XT and XS Series and other fully automated hematology analyzers.
Among many patients, the ratios and counts of the five types of white blood cell-lymphocyte, monocyte, neutrophil, eosinophil and basophil-differ from those found in the blood of healthy individuals. From the standpoint of diagnosing disease, it is extremely important to accurately classify and count white blood cells, including atypical white blood cells. However, under previously available measuring methods it was difficult to discern between normal and atypical white blood cells, making simultaneous classification and counting results difficult to achieve.
This invention involves the preparation of a solution of red blood cells and the development of a pigmenting compound. This compound substantially enhances fluorescent intensity by combining a hemolysis agent that renders the cells to be measured receptive to staining with the RNA included in the cells. Using these two elements facilitates the classification and counting of five types of normal white blood cell, simply by mixing the reagent with a blood sample. At the same time, atypical cells such as immature white cells are classified and counted, This invention also enables the automatic counting of immature granulocytes, which previously had been problematic.
As a result, extensive information on the measurement of normal and atypical white blood cells can be provided quickly. This invention has thus contributed to the efficiency of medical care and the early detection of blood disorders.
This invention also received the Invention Implementation Achievement Award, which is given to the representatives of companies recognized for their outstanding achievements in practical applications.
| Example 1: Normal Blood Analysis: Automated Hematology Analyzer and New Reagent 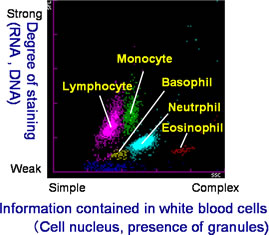 |
Example 2: Patient Blood Analysis: Automated Hematology Analyzer and New Reagent 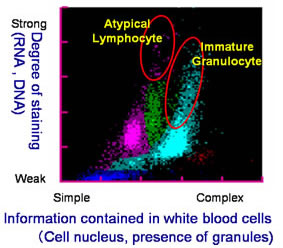 |
|
(2) Invention and Innovation Encouragement Award
Immunochromatography test sample preparation solution, immunochromatography testing method and immunochromatography test kit (Patent number: 4199606)
This is a sample preparation method and test kit for employing this method to achieve accurate tests employing immunochromatography.
Contracting influenza increases patient susceptibility to more serious diseases: among children, encephalitis; among seniors, pneumonia. The rapid provision of testing results is crucial in achieving accurate diagnoses.
Testing that employs immunochromatography involves taking a sample, and then staining a test device that includes the target antibody. It is a simple operation, but one that produces results. As no special instruments are needed, results can be obtained quickly on-location, making this method extremely effective in testing for such diseases as influenza.
However, influenza testing typically uses samples of mucus or other liquids that have been wiped from the nasopharynx. The mucins present in these samples are highly viscous, and can contain epidermal cells, which obstruct the pores of the porous membranes employed in testing devices. This can affect testing accuracy by causing testing to terminate midway or by producing aberrant results.
By treating the preparation sample with a solution that includes a non-ionic surfactant and an alkali metal ion in 0.3 mol/L or higher concentration, this invention eliminates the testing problems that can occur when using mucal samples, making influenza testing faster and more accurate. The technology employed in this invention is used in POCTEM Series immunochromatography diagnosis kits.
Fluid suction device (Patent number: 3771380)
This is a device that pierces through the cap that seals a container opening, using a suction tube to extract fluid from the container. This fluid suction device can be used for extracting liquid samples for sampling analyzers. Moving the suction tube vertically requires the application of a strong force. However, placing undue force onto a capped container not only hampers mobility but, depending on the vertical position of the container, the suction tube may hit the bottom of the container, potentially damaging the tube.
By using an auxiliary mechanism during vertical motion of the suction tube, this invention applies appropriate force to the suction tube, whether for an airtight container or for an open container. This enables fluids to be withdrawn from both airtight containers and open containers. This new technology is incorporated in our CA-7000 and CA-1500 coagulation analyzers.
Coagulation analyzer (Patent number: 3722570)
This is a coagulation analyzer, which measures the time taken for a blood sample (specimen) to coagulate after the addition of a reagent.
In general, because the blood coagulation reaction undergoes a complex process, in some samples unstable cases may exist in which the reaction appears to have temporarily stopped midway through the process (saturation). This invention, when it detects that changes in scattered light intensity have stopped, observes the sample for a given time to determine that the diffused light intensity has not increased further, and measures the final saturation value. This new technology is incorporated in the CA Series.
History of Commendation for Invention awards received (2005-2010)
2009 Kinki Local Commendation
'Director-General of the Kinki Bureau of Economy, Trade, and Industry Award': Reagent for Analyzing Formed Elements in Urine
'Invention and Innovation Encouragement Award': Image Filing System, Reagent for Measuring Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Antiphospholipid Antibody Measuring Method and Blood Analyzer
2008 Kinki Local Commendation
'Commissioner of the Japan Patent Office Invention Incentive Award': HCV Reagent and HCV Antibody Detection Method
'Incentive Award': Particle Image Analyzer, Reagent and Method for Erythroblast Classification and Counting, Automatic Sample Preparation Apparatus
2007 Kinki Local Commendation
'Shibucho Award': Automated Sample Analytical Method and Instrument
'Invention and Innovation Encouragement Awards': Urinary Erythrocyte Differentiation Instrument and Method, Automated Analytical System and Method
2006 Kinki Local Commendation
'Shibucho Award': Non-Invasive Hematology Analyzer
'Invention and Innovation Encouragement Awards': Pipette Cleaner
2005 Kinki Local Commendation
'Commissioner of the Japan Patent Office Invention Incentive Award': Reagent and Method for Measuring Reticulocytes
- Information contained in the news release is current as of the date of the announcement,
but may be subject to change without prior notice.
